When many people hear the word "logistics," they imagine a storage location such as a logistics center or warehouse, or they think about transportation and delivery using large trucks packed with cargo and container ships traveling between ports. However, these are a result of incomplete understanding that captures only a small portion of logistics. This content reintroduces the essence of logistics in different aspects and its different forms.
Logistics actually has many roles. The most well-known role of logistics is sales logistics that moves products from the producer to the consumer. In addition to sales logistics, logistics can also be split into four other roles depending on the field. These are procurement logistics, production logistics, recovery logistics, and recycling logistics.
Procurement Logistics
Procurement logistics is the procurement of materials needed to manufacture products. It is sourcing of inventory needed to meet demand.
This could include raw materials needed to manufacture custom products or to sell to another business (also called production inventory), or finished goods that are ready to sell directly to the end consumer.
Once goods are sourced and received, they are then considered inventory, which involves the process of storing, managing SKUs, preparing items for retail fulfilment, and ordering more to replenish inventory.
Production Logistics
The term is used for describing logistic processes within an industry.The purpose of production logistics is to ensure that each machine and workstation is being fed with the right product in the right quantity and quality at the right point in time. Production logistics can be applied in existing as well as new plants. Manufacturing in an existing plant is a constantly changing process. Machines are exchanged and new ones added, which gives the opportunity to improve the production logistics system accordingly. Production logistics provides the means to achieve customer response and capital efficiency. Guiders students on successful completion of the course have been placed in manufacturing companies like KITEX, INTERGROW BRANDS(SYNTHITE) to name a few
Recovery Logistics
If the flow of goods from production to consumption by procurement logistics, production logistics, and sales logistics is described using the circulatory system of the body, it would be said to be forward logistics. On the other hand, recovery logistics or reverse logistics is the flow that recovers and recycles products, containers, and packaging that have fulfilled their role.
Recycling Logistics
Typical examples of recycling logistics are recovering and recycling empty cans, plastic bottles, and old paper. Containers, packaging, old computers, and inkjet cartridges can also be recovered and recycled in the same manner. The importance of recycling logistics has been increasing in recent years as measures for the environment and to effectively utilize materials such as minor metals.
Role of logistics
The roles of logistics feature transportation/delivery, storage, packaging, cargo handling, distribution processing, and information processing, and many systems have been put in place to deliver products from the production location or factory to the consumer quickly and on time.
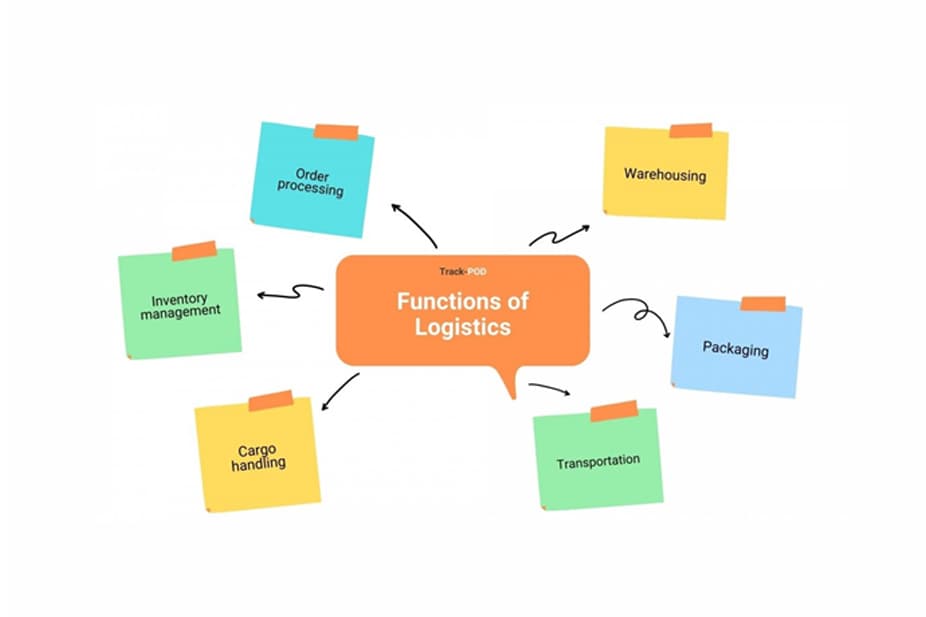
The functions of logistics below come in chronological order rather than in order of importance to logistics management. Therefore, transportation and the actual movement of goods come last on the list.
1. Order processing
Any delivery process can only function if there is an order processing system in place. Order processing systems vary from business to business. Either way, it's meant to support fast and effective information processing that kick-starts transportation activities. The key part of order processing in logistics management is integration. Customer-facing solutions, in perfect sync with the transportation management system (TMS) to make sure delivery of goods occurs at the right time and meets company and customer standards alike.
2. Inventory management
Inventory control is among the logistics functions that are often grouped together under the inventory/warehousing umbrella. Inventory refers to stocking finished goods in a storage facility. In order to support the transportation and delivery processes, inventory control requires information for maintaining inventory records, ensuring safety, predicting demand for goods and of course reordering stock.
Inventory logistics
Inventory logistics remains on the borderline between inbound and outbound logistics, as it involves both supplier relationship management (inbound logistics) and order fulfilment (outbound logistics). Therefore, inventory management is an important part of supply chain management and needs to be used efficiently.
Many of the students from Guiders education have been place in the Inventory department in Lulu International, Kochi and Trivandrum and with the strong foundation they received they have been doing their role well.
3. Warehousing
Warehouse management is a natural extension of inventory activities. At the warehouse level, handling, packing, and shipping workflows are established.
Both inventory and warehousing require sophisticated tools that support the main functions and help reduce costs via automation. Especially if your company delivers from multiple warehouses and needs complex logistical solutions.
TVS warehouse, Logiware, Yusen are a few of the companies who have employed guiders students in the role of warehouse executives
Warehousing transportation
Transportation management and delivery management software like Track-POD helps companies maintain control over the entire order fulfilment at the cost of a route planner.
For example, automated routing and route optimization can be done with unlimited departure locations, which means you can nail warehousing transportation activities and delight your customers with on-time deliveries from different warehouses.
4. Packaging
Packaging includes all the activities and operations implemented to prepare goods for handling and transportation to and from customers - in case of reverse logistics and returns specifically. Packaging is one major logistic function as it determines delivery success.
First and foremost, packaging needs to be compliant with safety and any customs regulations that may halt your delivery service. Moreover, it's important that packaging matches your storage and vehicle needs.
5. Cargo handling
Cargo handling is one of the major logistics activities that can't be overlooked when discussing logistics functions. It's closely related to packaging and determines logistical costs in a very real way.
Getting the package and handling procedures right is the foundation of physical distribution. It's equally important for safe storage and transportation. No consumer enjoys damaged products or the wrong product delivered to their door. No company wants ever-rising shipping costs because couriers have to make many trips to one customer to get the order right.
our students who have been placed in the TATA group, Big Basket have a major role to play in packaging and handling procedures in order to transport grocery, fruits vegetables etc to the consumer without any damage
6. Transportation
Last but not least is the transportation itself. Naturally, transportation is among the main logistics functions, if not the main. It's required at every step of every supply chain and the way companies build their transportation management system and functions determines the success of supply chain management.
Logistics companies employ our students transport co-ordinators and they do their job to perfection to ensure the smooth movement of goods from source to the consumer.
.